Java Notes:
JDK,JRE,JVM
diff
b/w jdk,jvm,jre
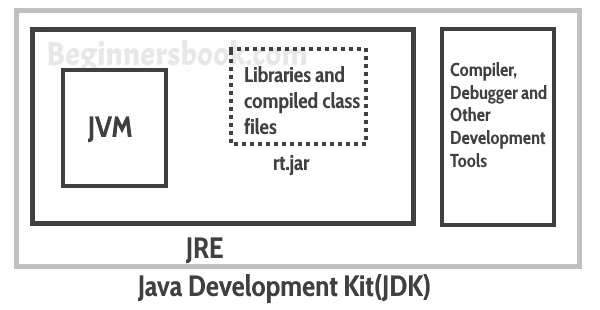
JDK: Java Development Kit
-
- Compiler: To create .class(byte codes) from the
.java file
- Debugger:
- package of Tools to develop java programs
JRE: Java Runtime Environment
-
- Java class libraries
- ClassLoader and Byte code verification
- package of Tools to run java programs
- loads compiled code to the memory and connects the code to
the appropriate java class libraries
JVM: Java Virtual Machine
- Java Interpreter : To run java programs
- JVM converts the bytecode into machine code.
- JVM is platform independent as JVM doesn’t depend on the
hardware and operating system of the machine.
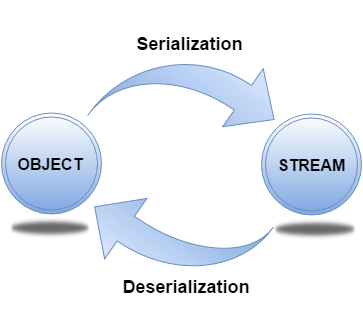
Serialization:
Marker Interface:
Serializable is a marker interface (has no data member and method).
It is used to "mark" Java classes so that the objects of
these classes may get a certain capability.
The
Cloneable and
Remote are also Marker interfaces.
It is used to
deliver type information at runtime to the JVM so that it can
take some action based on the information received
Serialization and DeSerialization:
The Serializable interface must be implemented by the class whose
object needs to be persisted.
The
String class and all the wrapper classes implement the
java.io.Serializable interface by default.
ObjectOutputStream class
The ObjectOutputStream class is used to write primitive data
types, and Java objects to an OutputStream. Only objects that support
the java.io.Serializable interface can be written to streams.
ObjectInputStream class
An ObjectInputStream deserializes objects and primitive data
written using an ObjectOutputStream.
serialization
java program example
String in Java
String
String is immutable and so you have to assign again to store
the result back to string variable after performing operations like strcmp,strcpy
etc.,
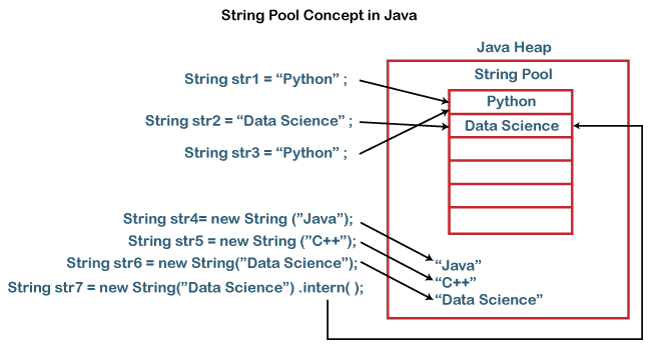
Literals saved in StringPool in java heap
memory.
JVM checks for each time when creating String object
in memory(string pool).
String literal is available in
(string pool)heap or not.If it is available it just returns object
reference to increase performance.
 String uses StringBuffer or StringBuilder to be mutable.
String uses StringBuffer or StringBuilder to be mutable.
StringBuffer
StringBuffer is mutable,thread safe,poor performance.
StringBuilder
StringBuilder is mutable,good performance but not thread safe
string
example program
Thread and Multithreading
Thread
Thread is a
path for execution.
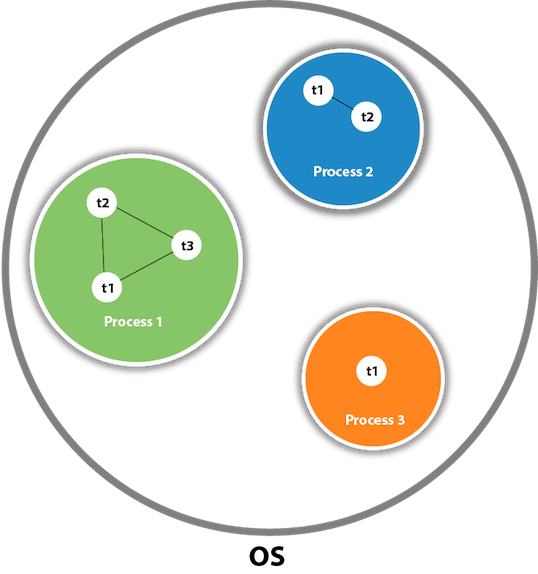
Thread States
Thread states: New,Runnable,Wait/Timely-wait/blocked,Terminated.
Multithreading
Multithreading refers to a process of executing
two or more threads simultaneously for maximum utilization of
the CPU.
A thread in Java is a lightweight process requiring fewer
resources to create and share the process resources.
Synchronization
Synchronization is the process of controlling other thread access when
execution of current thread.
thread
example program
OOPS Concepts
JAVA
Java is a high-level, class-based,platform independent,
object-oriented programming language that is designed to have as few
implementation dependencies as possible.
Object
A Java object is a
member (also called an instance) of a Java class.
Each object has an
identity, a behavior and a state.
he state of an object is stored in fields (variables), while
methods (functions) display the object's behavior.
Objects are created at runtime from templates, which are also
known as classes
Class
A class — in the
context of Java — is a template used to create objects and to
define object data types and methods.
Classes are
categories, and Objects are
items within each category.
Eg:
Vehicle car;
Encapsulation
Encapsulation in Java is a powerful mechanism for storing the data
members and data methods of a class together.
It is done in the form of a secure field accessible by only
the members of the same class.
Encapsulation in Java is the process by which
data (variables) and the code that acts upon them (methods) are
integrated as a single unit.
By encapsulating a class's variables, other classes cannot
access them, and only the methods of the class can access them.
Access Modifiers
- public(visibility in entire env)
- protected(visibility within package)
- private(visibility within its class)
Uses:
- Data hiding
- Flexibility
- Control and reusability
- Security
Polymorphism
Polymorphism means
"many forms", and it occurs when we have many classes that are
related to each other by inheritance.
Overloading and Overriding
When the
method signature (name and parameters) are the same in the
superclass and the child class, it's called overriding.
When
two or more methods in the same class have the same name but
different parameters, it's called overloading.
Inheritance
Inheritance in Java is the method to create a hierarchy between classes
by inheriting from other classes.
Java Inheritance is transitive -
so if Sedan extends Car and Car extends Vehicle, then Sedan
is also inherited from the Vehicle class.
The Vehicle becomes the superclass of both Car and Sedan.
- Single
- Multilevel
- Hierarchical
- Multiple(Not possible with class to class - so Interface
introduced)
Keywords
extends : class inherits class / interface inherits interface
implements : class inherits interface / vice versa
Abstraction
Data abstraction is the process of
hiding certain details and showing only essential information to
the user.
Abstraction can be achieved with either abstract classes or
interfaces.
The
abstract keyword is a
non-access modifier, used for classes and methods:
- Abstract class: is a restricted class that cannot be
used to create objects (to access it, it must be inherited from
another class).
An abstract class can have both abstract
and regular methods
- Abstract method: can only be used in an abstract
class, and it does not have a body.
The body is provided by
the subclass (inherited from).
Uses
Security
It can also acheives through interface.
Difference between Abstract class and Interface
An abstract class allows you to create functionality that subclasses
can implement or override.
An interface only allows you to define functionality, not
implement it but default method allows impl from java 8.
Non access Modifier Keywords
static
The static variable can be used to refer to the common property of all
objects (which is not unique for each object),
for example, the company name of employees, college name of
students, etc.
The static variable gets memory only once in the class area
at the time of class loading.
Access directly by class no need to create instance/object.
final
The final keyword is a non-access modifier used for classes, attributes
and methods, which makes them non-changeable (impossible to inherit or
override)
PassByValue and PassByReference
PassByValue refers that the value of variable to be passed while method
calling.
PassByReference refers that the reference(memory) of variable
to be passed while method calling.
Java by default supports
pass by value for
primitive types whereas for
objects it is
pass by reference.

 String uses StringBuffer or StringBuilder to be mutable.
String uses StringBuffer or StringBuilder to be mutable. 


